In forex, timing is everything. If I had written this post a couple weeks ago, the headline would read “Euro Touches 2009 High.” Perhaps if I had waited another week, it would have read, “Euro Approaching 2009 High.” But alas, I chose today to write about the Euro, and the headline I chose is probably the most appropriate under the circumstances.
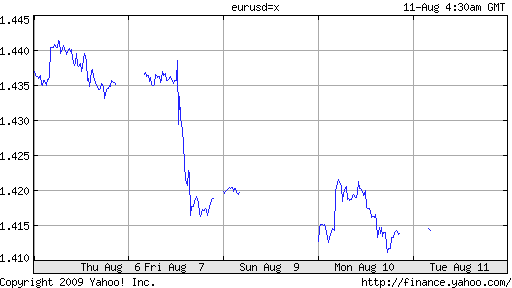
On August 5, “The euro hit a high for the year against the dollar as stocks trimmed their losses in afternoon trading Wednesday despite a generally cautious tone in currency markets.” Analysts were careful to point out that the markets remained cautious and the Euro eased past - rather than smashed through - its previous high.Technical analysts would and have argued that this paved the way for the subsequently rapid decline: “The euro is testing the base of an ascending channel with daily momentum charts showing a ‘double top in overbought territory.’ ”
This notion might have some merit, considering that fundamentals arguably favor a continued Euro appreciation. “The economy of the 27-country European Union shrank 0.3 percent in the three months ended June 30, for an annual rate of roughly 1.2 percent. The 16 countries that use the euro registered a 0.1 percent decline for the second quarter, or an annual rate of roughly 0.4 percent.” While output remains well below its 2008 levels, the slight contraction represents a tremendous improvement from the first quarter, when GDP shrank by 2.5%.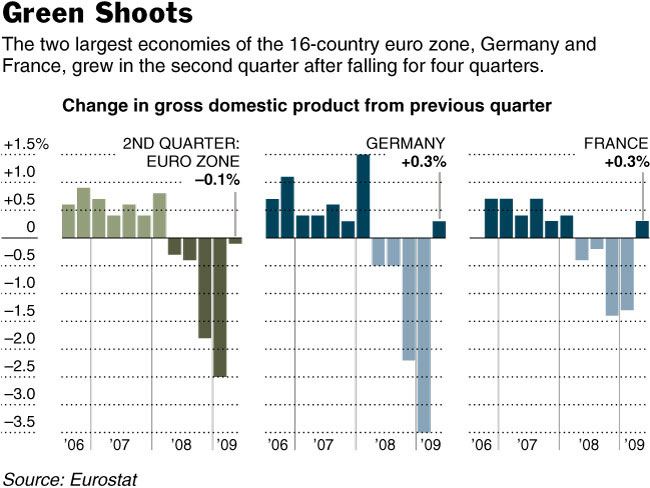
“Underlying the strong reading were solid performances in France and Germany, each of which grew 0.3 percent in the second quarter, government data showed.” This is helping to offset further contractions in Italy and Spain, which have turned into economic laggards as a result of the housing bust. In addition, exports in Germany grew by 7% last month, and “Investor sentiment improved more than analysts had expected in August to its best level since April 2006.” On an aggregate basis, “the euro zone’s trade balance with the rest of the world rose to 4.6 billion euros ($6.5 billion) in June, compared to a flat balance in the same month last year,”
Still, explorers looking for bad news and/or cracks beneath the surface will have no difficulty finding them. German exports (and output in general remain down year-over-year. In addition, there are still trouble spots in the EU, notably in western Europe. “Already, the euro area’s unemployment rate stands at 9.4 percent, its highest level in 10 years, and the anemic growth of the coming quarters will not be enough to arrest the slide. That, in turn, could drag down consumer confidence or even generate political backlash in Europe, economists said.” Most worrying is perhaps that, “consumer prices in the euro area dropped 0.6 percent in July…” ‘Deflation is becoming entrenched in the euro area, which would be very bad for the economy.’ ” Good thing the ECB left some room to lower rates further.

AUGUST 17TH 2009
The Force is With the Yen
Just when it looked like the carry trade was back for good and all signs pointed to a Yen depreciation, out of nowhere came a series of surprise developments, propping the Yen back up. Spanning finance, economics, and politics - a Forex Trifecta - these developments moved swiftly through the markets, creating optimism for the Yen where before there was only pessimism. Of course, it’s possible that this bump will prove temporary, and a reversal could transpire just as quickly.
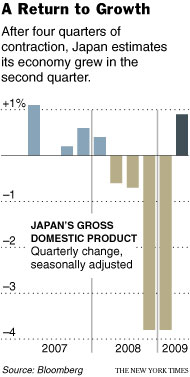
The biggest news, by a large margin, was a report that the Japanese economy had returned to growth. Similar in scale and in tenor to stories coming out of other countries, the data showed that Japan grew at an annualized rate of 3.6% in the second quarter of 2009, a sharp reversal from the 11.7% contraction in the previous quarter (which was itself revised upward from -14%).
The sudden sea change was brought about by a combination of government spending and export growth. “New tax breaks and incentives to help sales of energy-efficient cars and household appliances, coupled with lower gas prices and a rebound in share prices, spurred consumer spending. Prime Minister Taro Aso has pledged 25 trillion yen (about $263 billion) in stimulus money, including a cash handout plan and more public spending on programs like quake-proofing the country’s public schools, to revive the economy.” Meanwhile exports grew by a healthy 6.3% from the previous quarter, while imports fell, causing the trade surplus to widen.
The announcement of economic recovery was accompanied by a noteworthy reversal in capital flows, such that Japan’s capital account swung into surprise weekly surplus: “Foreign investors bought 292.9 billion yen ($3.1 billion) more Japanese stocks than they sold during the week ended Aug. 8 and domestic investors were net buyers of 125 billion yen in overseas bonds and notes.” Meanwhile, speculation is mounting that Japanese investors will move to repatriate some of the coupon and redemption payments they receive on their US Treasury investments.
While seemingly unrelated to the economic turnaround (it’s important not to read too much into weekly data), this could be a sign that Japanese investors are growing more optimistic about domestic economic prospects and are moving to invest more at home. It’s worth noting that such a shift could actually be necessary if the recovery is to be sustained, in order to increase the role of (capital) investment, relative to exports and government spending. Ironically, it could instead be a sign of excessive pessimism, if Japanese believe that prospects for US/global growth have been overestimated, in which case risk appetite and the carry trade would be due for a combined correction.
Domestic consumption could also play an increasing role in Japan’s economy going forward, as a result of imminent political changes. “To stimulate consumption at home, the Democrats have pledged to put more money in the hands of consumers by providing child allowances, eliminating highway tolls and making fuel cheaper. That marks a shift away from the long-ruling LDP’s emphasis on steps to help companies.”
Along similar lines, the Democratic Party (which has a wide lead over the incumbent Liberal Democratic Party), has also conveyed its opposition to currency intervention, since such tactics inherently prioritize export growth over domestic consumption. “Japan’s export-led growth is reaching its limits and Tokyo should not intervene in markets to weaken the yen as long as currency moves match fundamentals, the No.2 executive in the main opposition party said on Monday.” Could the carry trade be in trouble?












Thanks for this article. The only thing i dont like about is the color of your blog... red is to strong, and i can't even event reading your post. Buy QMobile Noir A700 in Pakistan
ReplyDelete